Topics to cover:
Examples of Vector Art
Opening
Saving
Place
If you would like to place an image into an already open document, hit Command+D, or File>Place.
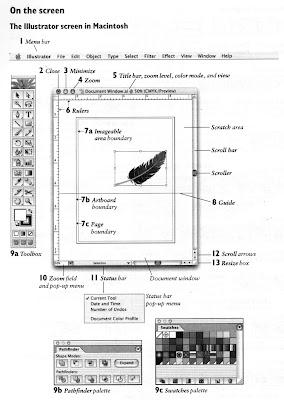
Artboard
ArtBoard: Printable Area
Working area: All shapes and images will save with the file, but they won't be printable.
*To change the artboard size, go to File>Document Setup>Artboard
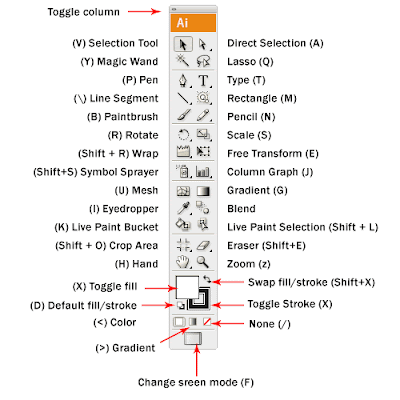
Toolbox
-Selection Tool
-Direct Selection Tool
-Rectangle, Ellipse, Polygon, Star Tools
-Fill and Stroke
-EyeDropper
-Pen Tool
-Align Objects
Collapsable Panels
Swatches
Use the swatch panel to choose and store default and user defined colors
Template
In the layers panel, click on the drop down menu to the right of the word "Layers". Select template, then make a new layer. This will allow you to trace imported images.
To get a better view of what you are tracing, hit Command + Y to go into Outline Mode. Very helpful.
Shape Modes:
-Add: Joins the outer edge of selected objects into one compound shape. Think of it like adding to a silhouette.
-Subtract: Subtracts the shape of the object in front from the object in back while preserving the paint attributes of the backgrond object. Think of it like a cookie cutter.
-Intersect: Protects overlapping areas and removes areas that don't.
-Exclude: Removes overlapping areas and preserves everything else.
In Class Assignments:
1. First, follow along as I demonstrate a few key tools. Try and get a feel for each tool, and the logic behind illustrator. Think polygons and overlapping shapes. Familiarize yourself with zooming in and out, using the space bar and mouse to move around the document, and switching between full screen and regular mode. It's easy to get lost in Illustrator when you're zoomed in all the way, so watch out!
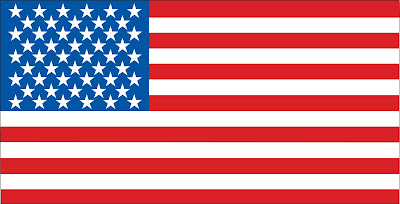
2. American flag (basic shapes)
-Using File>Place, bring up the American flag image.
-Turn it into a template in the drop down menu in the layers panel.
-On a new layer, use the swatch palette and the shape tools to recreate flag.
3. Space Invaders (pathfinder)
-Recreate the iconic Space Invaders using the pen tool, shape tools, and pathfinders.
4.Snowman
-Use everything we've learned today to build a snowman!